Comparing Implementation Variants Of Distributed Spatial Join on Spark
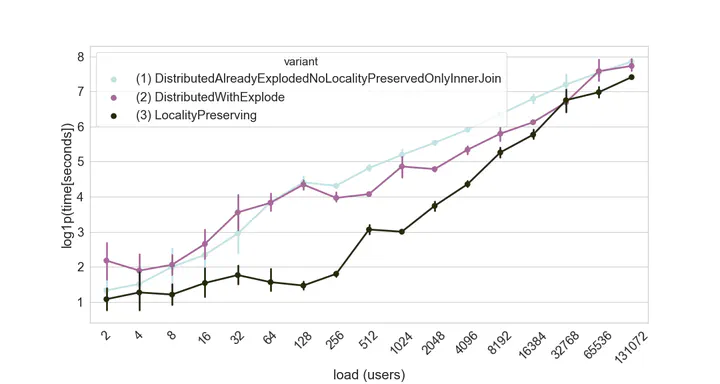 200 events per user per period for 3 periods. Load of users (x axis), processing time shown in logarithmic scale (y axis) for the 3 different implementations of a spatial join. Each one was run 5 times. The graph shows the mean and 95% confidence intervals as error bars.
200 events per user per period for 3 periods. Load of users (x axis), processing time shown in logarithmic scale (y axis) for the 3 different implementations of a spatial join. Each one was run 5 times. The graph shows the mean and 95% confidence intervals as error bars.Abstract
As an increasing number of sensor devices (Internet of Things) is used, more and more spatio-temporal data becomes available. Being able to process and analyze large quantities of such datasets is therefore critical. Spatial joins in classical geo-information systems do not scale well. Nevertheless, distributed implementations are promising to solve this. Various implementation variants for distributed spatial joins are documented in literature, with some being only suitable for specific use cases. We compared broadcast and multiple variants of a distributed spatially partitioned join. We anticipate that this comparison will give guidance to when to use which implementation strategy.
Type
Publication
Poster IEEE Big Data proceedings: Comparing Implementation Variants Of Distributed Spatial Join on Spark